
Bruce Nicayenzi, in Experimental Methods in Orthopaedic Biomechanics, 2017 5 DiscussionĪfter completing all screw pullout tests, data collection, data analysis, and data presentation, then final results can be considered and interpreted in the broader context of some important clinical, biomechanical, and/or technological considerations, as follows.
Further, work strings and smaller diameter casing strings have been employed in rotary drilling operations with success.īoth the hook thread in concert with a torque shoulder and especially the wedge thread with its self-contained thread profile torque resistance are suitable in minimizing the adverse effects accompanying torsion. The ability to rotate the tubular string (during cementing, for example) can positively affect the installation and survivability of a tubular. Both of these concerns-high induced stresses and interstitial movement during assembly-are either limited or eliminated by the presence of a torque shoulder. This coupling-to-pin relative movement, common to API buttress, casts further doubt on the leak integrity available in the threaded region. Further, thread profiles possessing gaps on the load and stab thread flanks (as opposed to the thread roots and crests) undergo a Poisson's ratio induced relative axial movement during assembly. Aside from reducing the box/coupling's resistance to a hydrogen sulfide environment, unchecked axial engagement during assembly can increase the risk of galling. Inasmuch as most threaded connections possess a positive thread taper, 32 assembly of the connection induces a positive hoop stress in the box/coupling and a negative hoop stress in the pin. Limiting axial displacement during assembly.
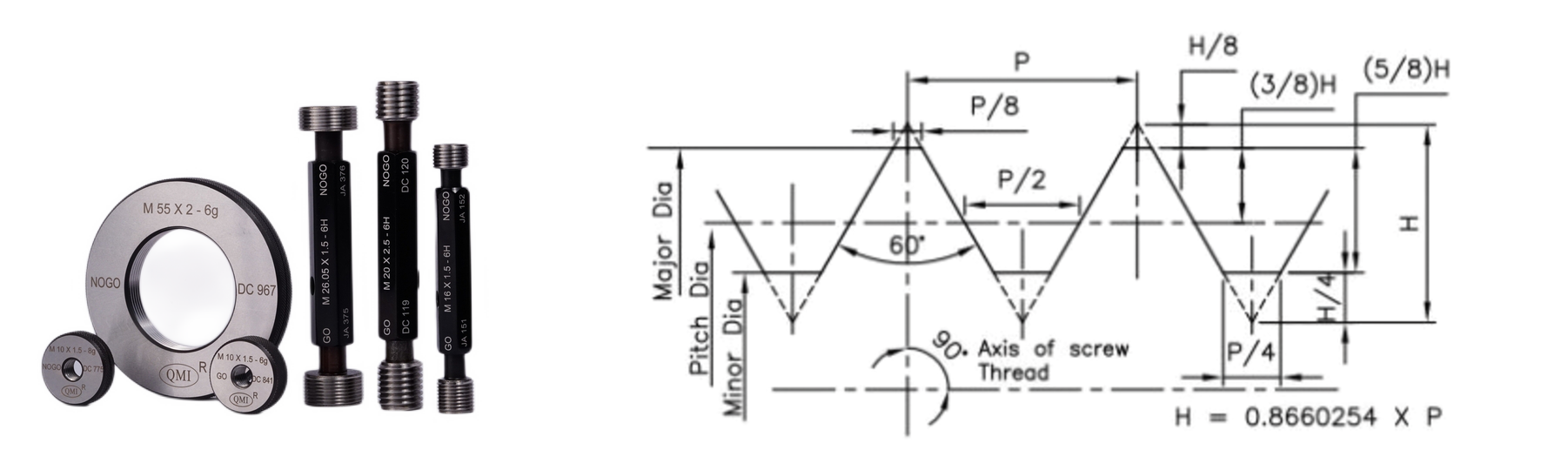
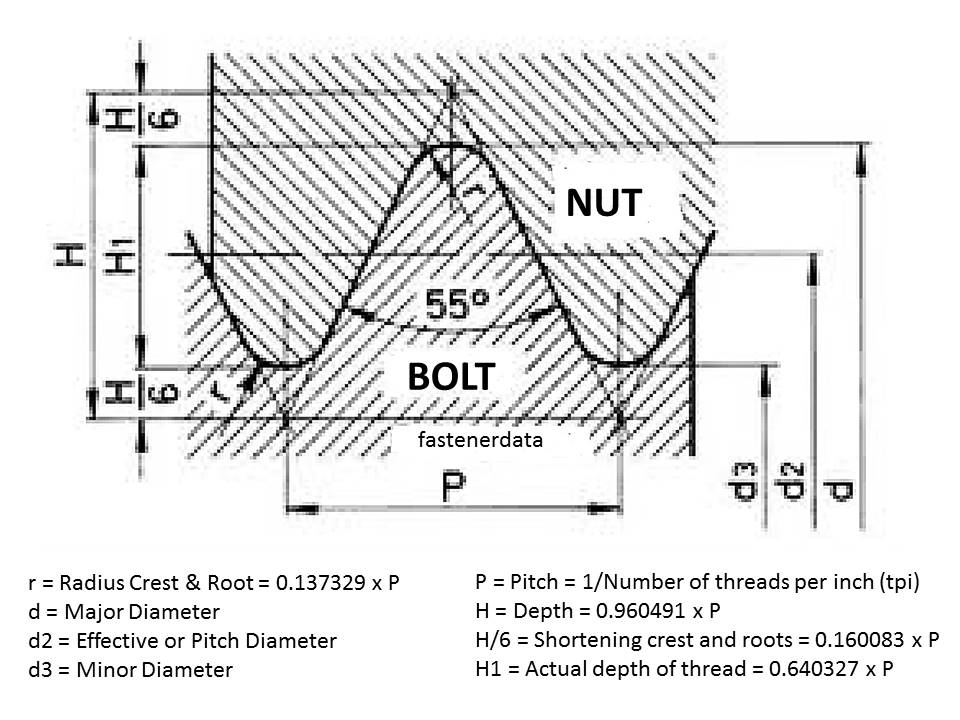
The existence of a torque shoulder enhances the structural resistance of a threaded connection in several ways: M16, then it is assumed that the coarse series thread is required. If a thread is dimensioned without reference to the pitch, e.g. On a drawing, a thread will be designated by the letter M followed by the size of the nominal diameter and the pitch required, e.g.

* The pitch of 1.25 mm for 14 mm diameter is to be used only for sparking plugs. If these are not suitable, choose from Column 2, or finally from Column 3. Note: For preference, choose the diameters given in Column 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
